Any person who knows a little about chemistry is aware of chemical bonds. The chemical bond is the force among the atoms in a substance or molecule, that responsible for the formation of any matter or substance. On the other side, the ionic bond is a type of bond between the atoms in molecules of ionic substance which consist of metal and non-metal atoms.
Ionic bond
The ionic bond is a chemical bond formed among the metal and non-metal substances. That means if a molecule consists of two atoms, then one of them must be a metal element and the other must be a non-metal element. There should be a transfer of electrons between the two atoms. The atom of metal element usually release electron and become a positive ion or cation, on the other hand, the non-metal element accepts electrons as well as become an anion. Then both ions attract each other and form a chemical bond which is an ionic bond. Therefore,
An ionic bond is a chemical bond that is formed by the process of transformation of electrons usually from the metallic atom to the non-metallic atom.
Ionic Bond Formation
As we learn in the above section, ionic bond formation is a process in which metallic and non-metallic elements take part, now in this section, we will try to understand how the ionic bonds are formed. The ionic bond formation is not that difficult processes to understand. It is really an easy and simple process so that it is added to the textbook of eight standard class.
Now, in process of ionic bond formation, a metallic element makes a chemical bond with a non-metallic element using the electrostatic force. This bond is formed, when a metallic element releases an electron and becomes a positive ion i.e. cation, on the other side the non-metallic element takes part to make the chemical bond, accepts the electron released by the metallic element, and becomes a negative ion, i.e. anion. After that, the positive cation and negative anion attract each other by the means of electrostatic force as well as a chemical bond which is called an ionic bond.
Explanation of Ionic Bond Formation with Example
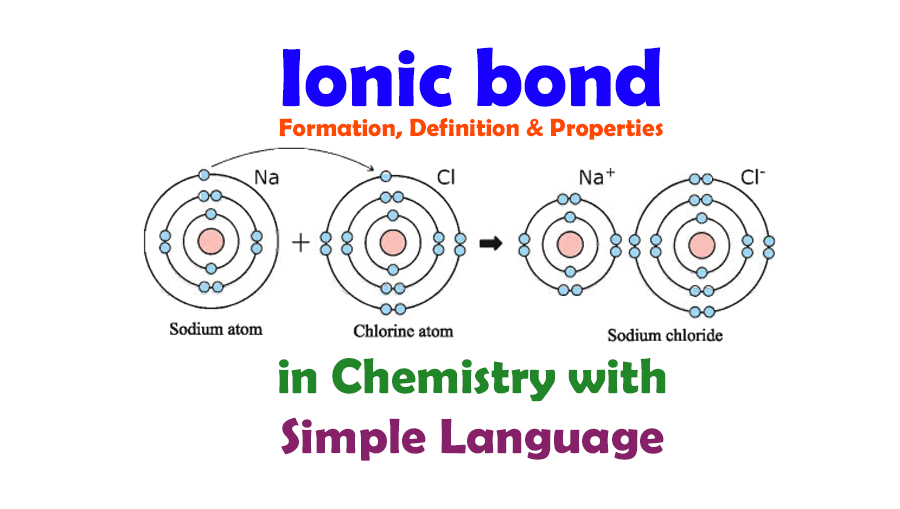
To make the processes understandable we are trying to give some examples for ionic bond formation. So here, we take a very simple ionic compound, NaCl, as an example to make the bond formation concept clear.
We all know that the sodium element consists of eleven electrons and the same number of protons. When the chlorine atom, Cl comes closer to form a chemical bond with the sodium atom Na, the sodium atom released the one electron in the outermost energy level as well as becomes a positive cation, Na+. It happens because the last electron of the sodium atom alone occupies its position in the third energy level. It remains single and far away from the center of the atom as well as by releasing this electron sodium can achieve the electronic configuration of the inert gas Neon, Ne, and this electronic configuration is very stable.
Electronic configuration of sodium, Na, is-
Na → 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
after releasing the electron,
Na+ → 1s2 2s2 2p6
electronic configuration of inert gas Neon is-
Ne → 1s2 2s2 2p6 (same as Na+)

On the other hand, the chlorine atom readily accepts the electron released by the sodium atom. Because the Chlorine atom has seventeen electrons among them seven electrons are in the outermost energy level. Therefore, to fulfill the octet of the chlorine atom it needs only one electron. So it takes up the electron and fulfills its octet as well as becomes a negative ion which means anion. At the same time when chlorine becomes an anion, it also achieves the electronic configuration of the nearest inert gas argon, Ar. As the electronic configuration of the chloride ion Cl- is the same as the inert gas argon, this electronic configuration is very stable.
Electronic configuration of Chlorine, Cl, is-
Cl → 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p5
after accepting the electron from sodium,
Cl– → 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6
electronic configuration of inert gas Argon, Ar, is-
Ar → 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 (same as Cl–)

At this stage, when the two ions, the positive sodium ion, and negative chloride ion come closer they attract each other very strongly by electrostatic force. Therefore, a chemical born is formed by this strong electrostatic force attraction force between the positive sodium ion (Na+) and negative chloride ion (Cl–). This chemical bond is ionic.
The phenomenon at a glance by equation is below-
Na → Na+ + e–
Cl + e– → Cl–
Na + Cl → Na+ + Cl– (NaCl)
Properties of the ionic bond or electrovalent bond
Ionic bonds are a very common and important type of chemical bond in chemistry. The properties or characteristics of the ionic bond or electrovalent bonds are discussed briefly below-
Melting and boiling point
The melting and boiling point of the ionic bonded compound is much higher than another compound. The ionic compound forms a crystal lattice, a large structure with a repeating cell. So the large crystal structure needs more energy to meltdown. Therefore the melting point and boiling point of an ionic compound are very high. For example, the melting point of NaCl is about 801° C, as well as the boiling point, is approximately 1,413° C.
Solubility
Apart from some exceptions, almost all ionic compounds are soluble in water. Water is a polar solvent as well as the universal solvent, so when the ionic substance dissolves in water it readily dissolves it.
The ions in the ionic compound make a large structure in form of a crystal lattice. There is an energy change when the crystal lattice is formed, which is called lattice energy. On the other side, there is an amount of energy needed to break down the lattice to dissolve it in water, which is known as hydration energy. If the hydration energy is greater and the lattice energy then the compound will dissolve in water.
When an ionic compound added to the water, the positive pole of the water attracts the negative ion of the ionic compound, as well as the negative pole of the water, attracts the positive ion of the compound and moves the positive ions and negative ions apart and surrounded them by making a sell of water.
Electrical conductivity
The ionic compounds in the solid form can not conduct electricity. Because the ions in the solid ionic compound are bound in a fixed place inside the solid structure. But when the solid ionic compound is dissolved in solvents or melted down, the ions of the compound can move from one place to another. Then it can conduct electricity. Therefore, in the melted or soluble condition the ionic compound can conduct electricity but not in the solid state.
Thanks for reading the article. Please share this article with your friends and help us to improve contains by inspiring us by sharing.
Follow us on Twitter, Facebook, Linkedin, and Tumblr
Read more
K2Cr2O7 + FeSO4 + HCl = KCl + CrCl3 + FeCl3 + Fe2(SO4)3 + H2O

Leave a Reply