Theory of Determination of Molecular Weight Of A Substance By The Cryoscopic Method :
The molecular weight of a substance can be determined by this method. It is a beneficiallmethodor an ordinary laboratory to determine molecular weight. The property of a solvent differs from those of pure solvents due to interactions that takes place between the solute and solvent molecules. Colligative properties are called the characteristics that show such modifications. The colligative properties are-
- Vapor pressure lowering
- Boiling point elevation
- Freezing point depression
- Change in Osmotic pressure etc.
The characteristics rely only on the number of particles dissolved in the solvent (molecules or ions). This determination of the molecular weight of a substance by the cryoscopic method will explain the phenomenon of the Freezing point depression. When the particular solute is dissolved in solvents, the following expression holds:
ΔT= T0f – Tf = Kf X m = Kf X (1000w1/Mw2)
The trams T0f and Tf refer to the freezing point temperature of the pure solvent and the solution respectively. The tram “m” refers to the molality Kf refers to the freezing point depression constant. It only depends on the solvents. (For Cyclohexane Kf = 20.2 deg. kg/mole of solute.)
Read some chemistry lab experiments

Apparatus and Chemicals needed for determination of the molecular weight of a substance by the cryoscopic method:
- Digital thermometer (-100C to 1000C )
- Stirring Rod
- Ice
- Stop Watch
- Cyclohexane
- Camphor etc.
Procedure for determination of the molecular weight of a substance by the cryoscopic method:
- Set up the apparatus ensuring that the stirrer does not touch the thermometer.
- Take 20 to 25 mL cyclohexane into the tube , placeit in the air jacket ,and dip it in the freezing mixture. Cool it by direct immersion in the ice bath until the cyclohexane starts to freeze.
- Take a thermometer reading every 30 seconds.
- Stir the cyclohexane slowly and take the thermometer reading until the constant reading is obtained.
- Take out the freezing tube and warm up with your hand until the solid melts.
- Add the measured quantity of (about 0.5 to 0.6 gm ) of the solute into the tube and dissolve it by stirring.
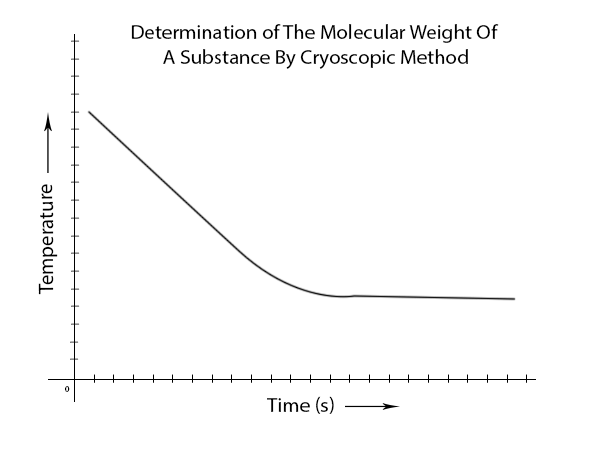
- Now again take the thermometer reading until the cyclohexane freeze and constant thermometer reading are obtained and Plot temperature against time for solvent and solute in the same graph.
- Now calculate the molecular weight of a substance by the cryoscopic method.
For your help, we give a screenshot of the taken datasheet and the plot:
Data:
1. Data for the pure cyclohexane –
| Time (min) | Temperature (0C) |
| 0.5 | a |
| 1.0 | b |
| 1.5 | c |
| 2.0 | d |
| 2.5 | e |
| 3.0 | f |
| 3.5 | g |
| 4.0 | h |
| 4.5 | i |
2. Data for cyclohexane after adding the solute-
| Time (min) | Temperature (0C) |
| 0.5 | j |
| 1.0 | k |
| 1.5 | l |
| 2.0 | m |
| 2.5 | n |
| 3.0 | o |
| 3.5 | p |
| 4.0 | q |
| 4.5 | r |
3. The plot for the above two data tables-

Calculation :
- The volume of the solvent = 25 mL
- Density of the solvent = 0.79 gm/mL
- So Weight of the solvent = (25 × 0.79) gm = 19.79gm
- Weight of the solute = 0.50gm
- Freezing point depression constant Kf = 20.2 deg.kg/mole
- Freezing point depression from the graph = (y-x)0C
Result:
- The molecular weight of the naphthalene is M= (1000×Kf ×w1)/(w2 × ΔT)
=(1000×20.2×0.5)/{19.79×(x-y)} gm/mole
The actual molecular weight of the naphthalene is 128.0 gm/mole
Follow Us On Facebook, Twitter, Linkedin, and Youtube.
Read more about-
Preparation of Molar and Normal Solutions and Clear Concept of Molarity

Leave a Reply